Our Focuses|Nature-based Solutions|
Nature and Biodiversity
Winbond recognized that preserving ecosystems and the natural environment was key to advancing sustainable development. In recent years, climate-related risks had become a focal point for stakeholders, and biodiversity loss had gradually emerged as a critical issue with significant impact.
In response to the Global Goal for Nature and biodiversity-related topics, Winbond proactively adopted the assessment methodology proposed by the Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD). In collaboration with the Chung-Hua Institution for Economic Research, Winbond followed the four-step LEAP approach—Locate, Evaluate, Assess, and Prepare—to gain deeper insights into the interdependencies between its Taiwan fabs and surrounding ecosystems. Through systematic analysis, Winbond identified nature-related risks and opportunities, integrated them into its Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) framework, and enhanced its risk control capabilities to ensure operational stability, safeguard stakeholder interests, and address the company’s reliance and impact on natural resources. Winbond further developed biodiversity conservation strategies. To mitigate environmental impacts from operations, Winbond committed to reducing its influence on nature through green product innovation and science-based carbon reduction. The company promoted biodiversity conservation and reforestation initiatives to take responsibility for alleviating its impact on the broader ecological environment. Internally, Winbond called on its value chain and operational sites to prevent deforestation, and continued to plan for avoidance, minimalization, and restoration measures. Nature-based Solutions (NbS) were systematically introduced to pursue the shared goals of No Net Loss and Net Positive Impact, striving to balance technological advancement with ecological preservation.
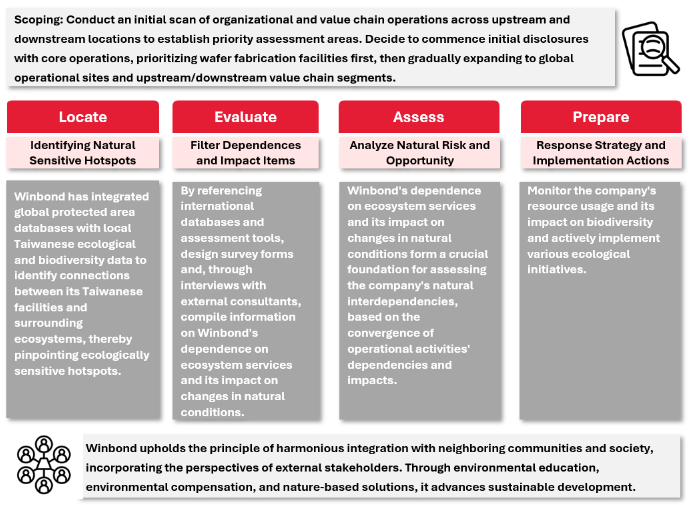
Locate Analysis: Identifying Nature-Sensitive Hotspots
Winbond conducted a "Locate Analysis" for its operational sites in Taiwan, beginning with the identification of areas with higher nature sensitivity. This facilitated subsequent evaluations of each site's dependence on and impact on nature, followed by risk and opportunity assessments. The evaluation process focused on operational sites and assessed nature sensitivity based on "location sensitivity" and "species sensitivity." It preliminarily identified the potential dependencies and impacts of operational activities on the natural environment and prioritized sites for further assessment accordingly.
- Location Sensitivity Analysis: Geographic overlay operations were performed using the "TGOS Geographic Information System" and the "National Ecological Green Network" to examine key statutory sensitive area layers, referencing data from the "IUCN World Database on Protected Areas." The analysis incorporated domestic conservation regulations such as the National Park Act and the Wildlife Conservation Act, and integrated government-announced ecological sensitive zones, conservation policies, and species hotspot data. This established a locally applicable and internationally aligned sensitivity assessment framework, enhancing the precision and credibility of the evaluation.
- Species Sensitivity Analysis: Conducted via the Ministry of Agriculture’s "Taiwan Biodiversity Network (TBN)" and "Taiwan Biodiversity Information Access (TBIA)," the analysis investigated the presence of protected, endangered, or critical species within a 2-kilometer radius of each operational site. Evaluation criteria included species listed under the Wildlife Conservation Act and the national red list, with higher-level classifications used for categorization and scoring to ensure representativeness and accuracy of the results.
Locate Analysis Evaluation Process
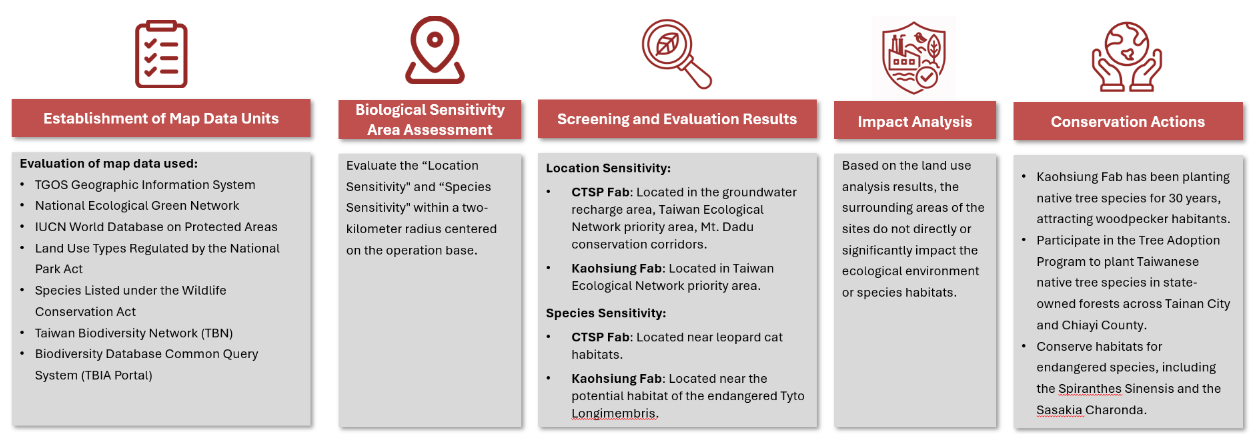
Location Sensitivity Analysis
Evaluate Analysis: Screening of Dependency and Impact Factors
For the identified operational sites during the Locate phase, Winbond further assesses the organization's dependence on natural capital and ecosystem services within its operational activities, along with potential impacts, based on industry characteristics, departmental functions, and activity specifics. Utilizing the ENCORE tool, factors related to natural dependencies and impacts associated with operational activities are screened and selected. The results indicated high dependency on water resources, climate regulation, and supporting services. Key impact topics included waste management, greenhouse gas and air pollutant emissions, and the use of freshwater and marine resources.
Assess Stage: Analyze Nature-related Risks and Opportunities
Based on the dependencies and impacts identified during the Evaluate stage, Winbond assessed potential future nature-related scenarios and evaluated the risks and opportunities arising from ecosystem service dependencies and nature impacts under each scenario. The assessment process was as follows:
Stage | Process | Task | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Collection | Compile Nature-related Risk/Opportunity List | Based on the Evaluate step analysis and internal/external information, compiled a list of relevant risk and opportunity topics. |
| 2 | Identification | Conduct TNFD Workshop | Departments assessed nature-related risks and opportunities based on business dependencies and impacts, and evaluated their influence across the upstream and downstream value chain. |
| Consolidate Identification Results | The working group consolidated nature-related risk and opportunity factors relevant to each department's operations. | ||
| 3 | Recognition | Nature-related Risks/Opportunities | Considering industry characteristics and operational conditions, identified Winbond’s nature-related risks and opportunities. Based on operational dependencies and impacts, set corresponding indicators and conducted pathway analysis to derive risks and opportunities. Evaluated financial impacts and formulated response strategies, continuously implemented risk mitigation measures and captured opportunities. |
Nature-related Risk and Opportunity Analysis
Winbond followed the TNFD (Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures) guidelines and integrated industry characteristics and operational realities to systematically identify nature-related risks and opportunities through the “TNFD Workshop.” The assessment results indicated that access to “renewable energy” and “reclaimed water” were the current major challenges. To reduce dependency on natural resources, the company continuously improved energy and water efficiency and actively expanded the procurement of renewable energy and the use of reclaimed water. The nature-related risks assessed in this stage were categorized into physical risks and transition risks. Physical risks included climate change-induced disasters, degradation of ecosystem services, and decline in air filtration functions. Transition risks encompassed changes in policy, market, technology, and reputation, and extended to liability risks potentially triggered by environmental pollution. Regarding nature-related opportunities, Winbond focused on enhancing resource efficiency, developing green products and services, expanding new markets, optimizing capital flows and financing mechanisms, strengthening corporate reputation and sustainable resource utilization capabilities, and promoting ecosystem protection, restoration, and regeneration strategies.
Prepare Phase: Strategic Response and Action Execution
Winbond adopted the AR3T action framework to mitigate its impact on biodiversity and incorporated the TNFD (Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures) framework into its sustainability strategy. Through the four principles of “Avoid,” “Reduce,” “Restore,” and “Regenerate,” the company systematically managed interactions between its operations and the natural environment, aiming to comprehensively assess financial impacts and promote sustainable operations.






