Our Focuses|Climate Change Management|Climate Risk Management
Climate Risk Management
Risk Management Framework
Winbond established the Risk Management Committee, under the Board of Directors to implement risk management, formulating a sound set of internal regulations and operating procedures through the Committee’s subdivisions or responsible units in accordance with their scope of operations.
For details, please refer to Risk Management under Corporate Governance.
Procedures for Identifying Climate Change Risks and Opportunities
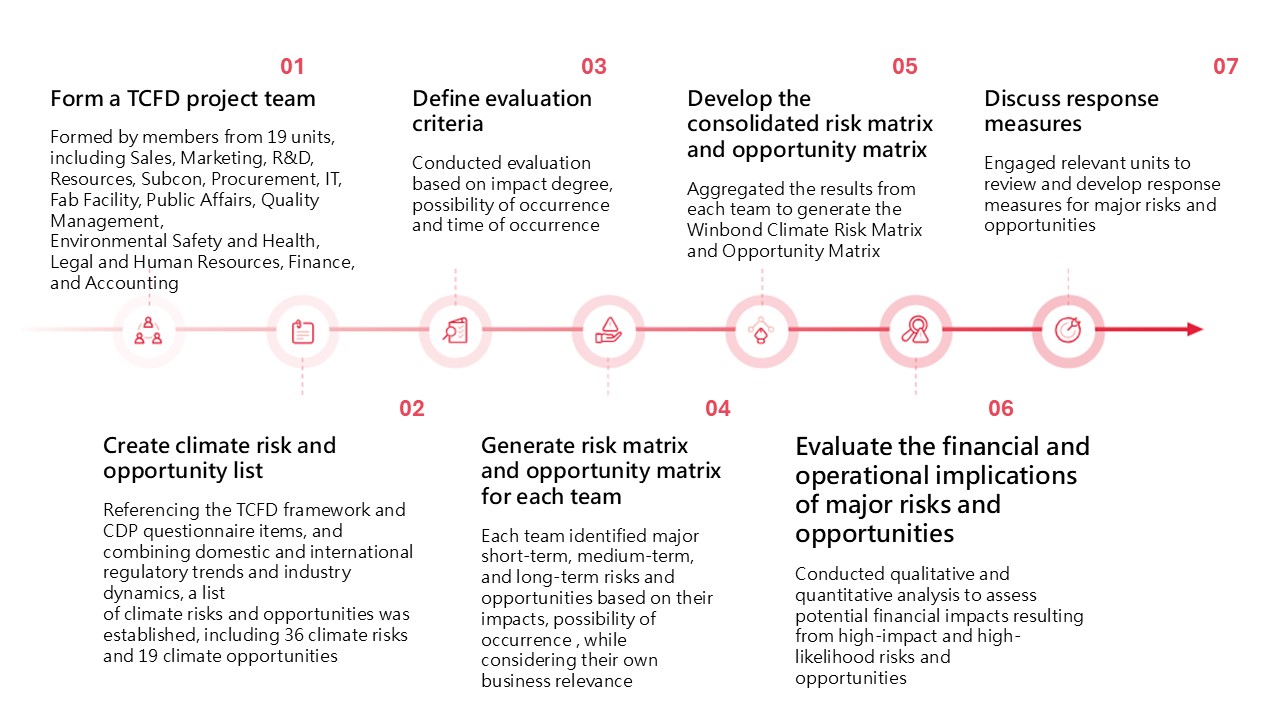
In 2024, Winbond convened 19 department-level units and over 30 members to establish the TCFD project team. The team members were grouped according to the nature of their business, and each group discussed climate change issues relevant to their business. They used Winbond's internally developed TCFD platform to identify climate risks and opportunities, generate matrixes. the team identified 3 major climate risks and 6 minor climate risks, as well as 3 major climate opportunities and 3 minor climate opportunities from 36 climate risks (including transition risks such as policy and regulations, technology, market, and reputation, and physical risks such as acute and chronic) and 19 climate opportunities (including resource efficiency, energy sources, products/services, markets, and resilience).
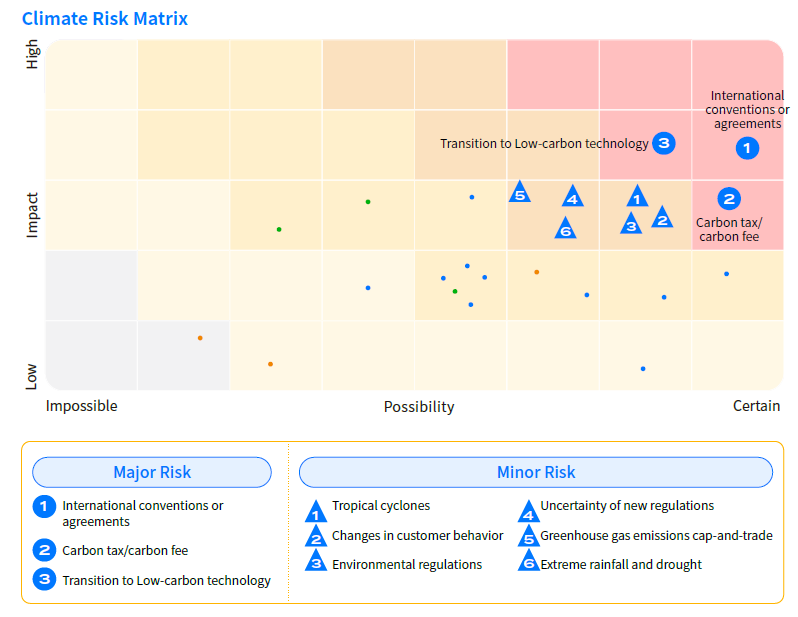
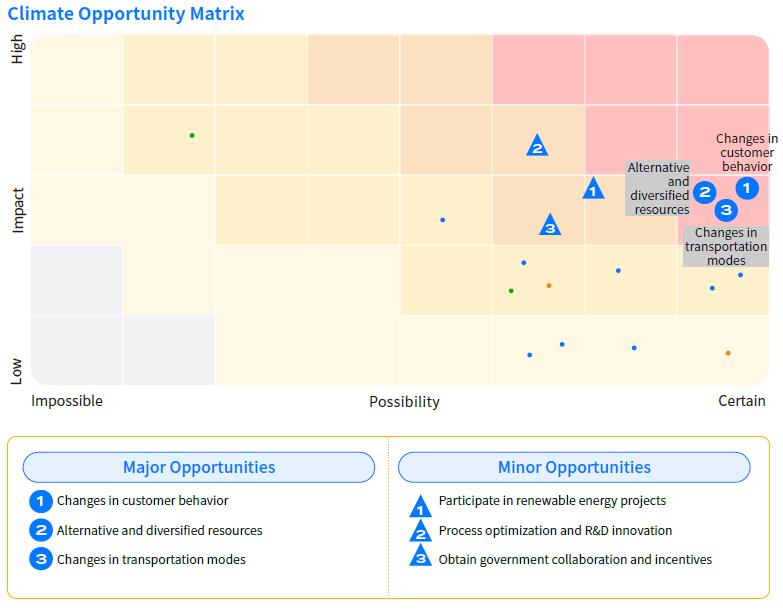
Climate Risk and Opportunity Matrix
Impacts of Major Climate Change and Responses
Major Climate Risks
(-) represents a negative impact, (+) represents a positive impact
| Cimate Risk | Time of Occurrence | Value Chain | Potential Financial or Operational Impacts | Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low-carbon technology transformation | Short-term |
|
|
|
| Carbon tax / Carbon fee | Short-term |
|
|
|
| International conventions or agreements | Short-term |
|
|
|
| Tropical cyclones | Short-term |
|
|
|
| Due to the implementation of the aforementioned measures, the estimated management costs for 2024 are as follows: | ||||
|
| |||
|
| |||
|
| |||
| Note: The primary climate risks identified in 2024 were all transition risks. Considering the completeness of the climate risk assessment, the "tropical cyclones," which had the highest impact and likelihood among the physical risks in 2024, was included in the assessment. | ||||
Major Climate Opportunities
| Climate Opportunity | Time of Occurrence | Value Chain | Potential Financial or Operational Impacts | Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Changes in customer behavior | Short-term |
|
|
|
| Alternative and diversified resources | Short-term |
|
|
|
| Changes in transportation modes | Short-term |
|
|
|
| Due to the implementation of the aforementioned measures, the estimated management costs for 2024 are as follows: | ||||
|
| |||
|
| |||
|
| |||





